Running a HTTPS website with Let's encrypt (for free)

Intro
Yes, you may have your website running HTTPS without having to pay for a SSL/TLS certificate.
Prerequisites
But first you need a working domain name, pointing to your web server. In other words, it is required to have your site running at http://your-domain-name.com first. For now, just http.
Using free certificate with ACME certbot
There are some different ways that will enable you to use Let’s Encrypt free certificates. And in this post, i will guide you to use certbot to both retrieve a SSL certificate and also renew it automatically before it gets expired.
Step 1: Go to Certbot website
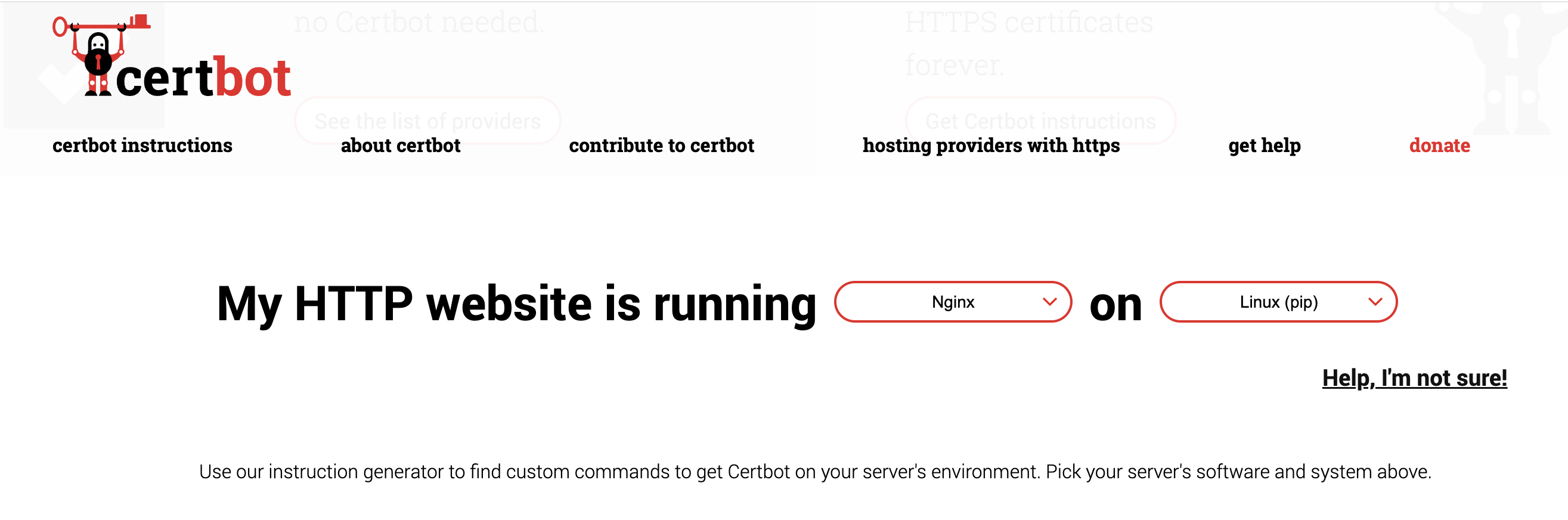
Step 2: Select software configuration
My server configuration is nginx running on a RockyLinux server. So, the selection should be
nginxas the softwareLinux (pip)as the platform. I want to use python pip as the package manager to install other tools.
Step 3: Install dependencies
With that selection being in place, certbot website guides me to install some dependencies before i can actually have certbot running
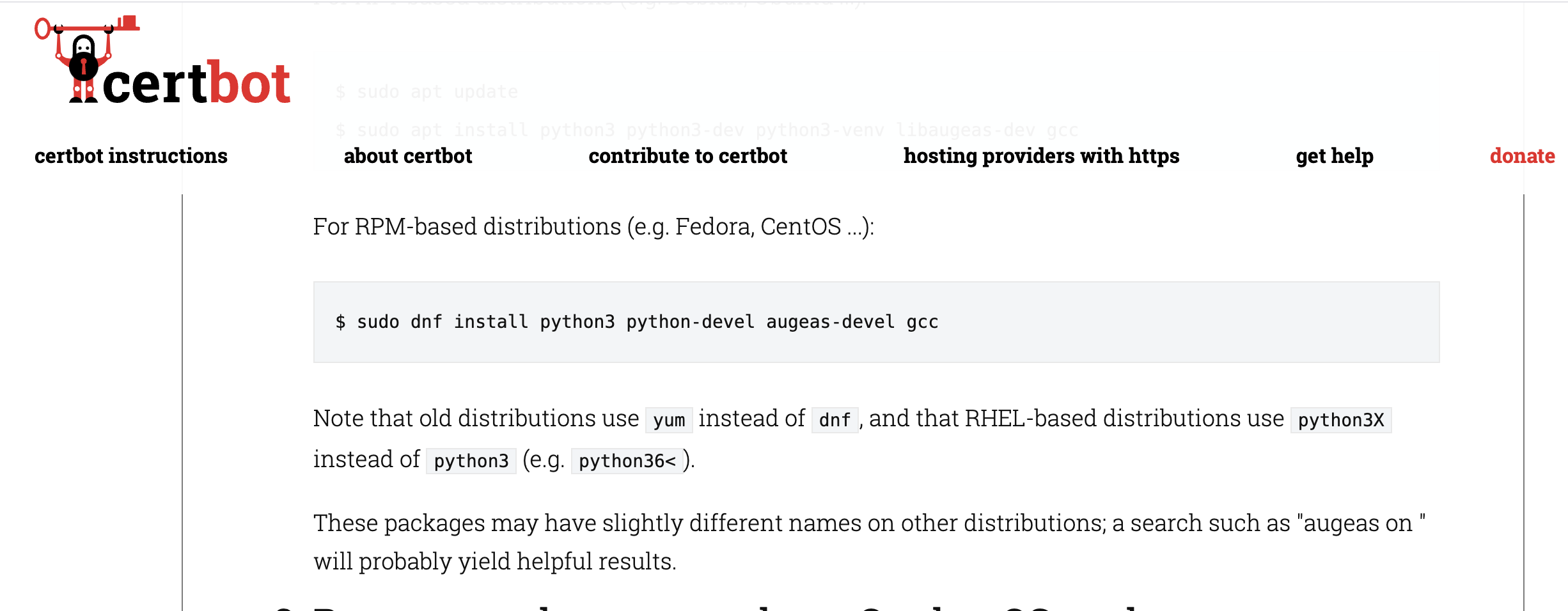
So, i just go ahead and run
|
Step 4: Remove old certbot package (if there is any)
|
Step 5: Setup python virtual environment
|
Step 6: Install certbot using pip
|
Step 7: Link the certbot command
So that it will be available whenever you type certbot in your command prompt
|
Step 8: Obtaining first certificate
I want cerbot to obtain the certificate and edit nginx configuration automatically, so I will issue this command:sudo certbot --nginx
certbot is going to repond with a messsage:Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
And if you run certbot for the first time on the machine, it will ask you for an email, in case they need to contact you.
|
And then it will ask you to read and agree with the terms of service:
|
An other interactive question:
|
|
At this step, it is expected that there already is a server configuration in your nginx config, something that should be similar to this:
|
And you now should enter your domain name in answer.
|
Now, you may verify the result of certbot action by reviewing nginx configuration file.
You may notice that certbot has automatically added a redirect configuration if there is a request to you site using http:
|
And it also add a server block to handle https traffic:
|
Congratulations!
Your website with SSL/TLS certification is ready.
Try going to your website by entering only domain name (that is http), you will be redirect automatically to the https site.
Part 2: Auto renew your certificate
Every certificate issued by Let’s Encrypt has a validity period of 3 months. So i will try to renew it once everymonth.
The idea is to simply use crontab to run the renew command automatically.
Create the script for auto renew
|
Paste following content into that file:
|
The script prints a date, so that a timestamp is logged for an easier debbuging. Then followed by certbot renew -q which is the heart of this script, it renews all certificate managed by certbot quietly, without any interactive question.
All error and output (2>&1) are written to the log file.
Add execute permission to the file
|
Set a schedule to execute this task
Certbot website guides users to run this script at 0 and 12 o’clock, plus a random amount of time in the range of 1 hour. So i will avoid this time range and choose an other time slot.
|
|
Because my certificate is issued on 26, so I decide to renew it on day 26 each month. And run it at 15:00.
With this setup, my website will have HTTPS certificate automatically.